Sulfur has been a foundational element in chemical manufacturing for more than a century. Today, its importance is greater than ever. From fertilizers and polymers to pharmaceuticals and energy materials, sulfur applications support a wide range of industrial processes that keep global supply chains moving.
As manufacturers face increasing pressure to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and meet tighter regulatory standards, sulfur-based products continue to evolve. This article explores how sulfur is used in modern chemical manufacturing, why it remains indispensable, and how companies can optimize its application across different sectors.
Why Sulfur Remains a Critical Industrial Element
Sulfur’s value lies in its versatility. It can act as a reactant, catalyst, stabilizer, or structural component depending on the application. Chemically, sulfur offers multiple oxidation states, allowing it to participate in a wide range of reactions.
In manufacturing, sulfur is also relatively abundant and cost-effective compared to many specialty elements. This combination of performance and availability makes sulfur-based products attractive for large-scale industrial use, particularly in regions with strong agricultural, energy, or materials industries.
Sulfur Applications in Fertilizer Production
One of the most significant sulfur applications is in fertilizer manufacturing. Sulfur is an essential plant nutrient, playing a key role in protein synthesis and enzyme function. As soil sulfur levels decline in many regions due to intensive farming, demand for sulfur-containing fertilizers continues to rise.
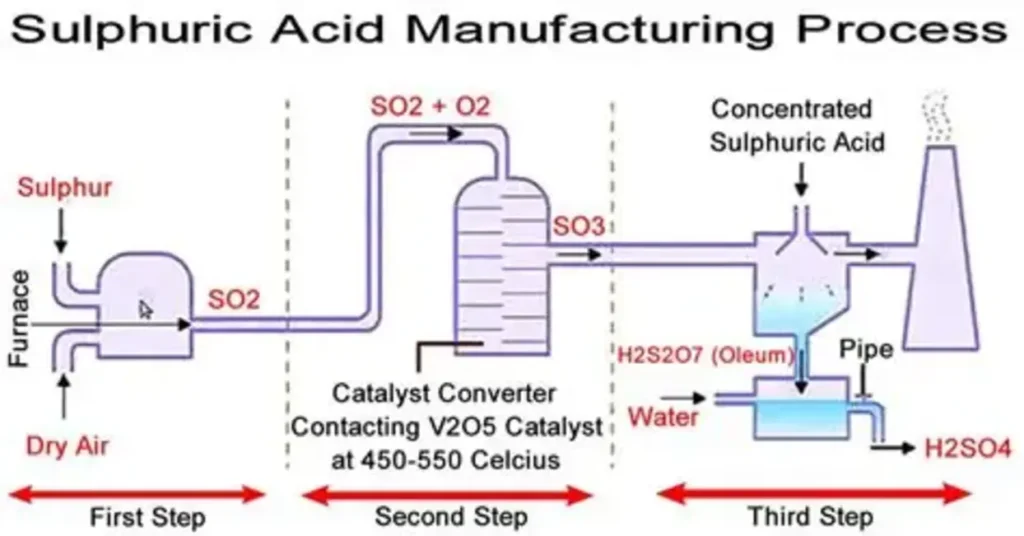
Common products include sulfuric acid and sulfate-based compounds such as ammonium sulfate. These materials improve nutrient uptake and soil health while supporting higher crop yields. For fertilizer manufacturers, using high-purity sulfur inputs helps ensure consistent product quality and predictable performance in the field.
Sulfur in Chemical Processing and Intermediates
Sulfuric acid is often called the backbone of the chemical industry, and for good reason. It is used extensively in the production of chemical intermediates, dyes, pigments, detergents, and industrial cleaners.
In many processes, sulfur-based reagents improve reaction efficiency or enable pathways that would otherwise be impractical. For example, sulfonation reactions are critical in producing surfactants used in household and industrial cleaning products. Reliable sulfur inputs are essential to maintain process stability and control operating costs.
Role of Sulfur in Rubber and Polymer Manufacturing
Another major area of sulfur applications is rubber and polymer production. Sulfur is a key component in vulcanization, the process that gives rubber its strength, elasticity, and durability.
In tire manufacturing, industrial hoses, seals, and conveyor belts, precise sulfur dosing directly affects product performance and lifespan. Modern manufacturers increasingly rely on specialized sulfur formulations that offer better dispersion, reduced bloom, and improved handling safety. These advancements help producers meet stricter quality standards while improving production efficiency.
Sulfur Applications in Pharmaceuticals and Fine Chemicals
In the pharmaceutical and fine chemicals sector, sulfur compounds are used to synthesize active ingredients and intermediates. Many antibiotics, vitamins, and therapeutic agents contain sulfur as part of their molecular structure.
Because purity and consistency are critical in these applications, manufacturers require sulfur products that meet strict specifications. Controlled particle size, low impurity levels, and reliable supply are key considerations. Suppliers that understand regulatory requirements and quality assurance processes play an important role in supporting pharmaceutical production.
Energy, Batteries, and Emerging Technologies
Sulfur applications are expanding into newer technologies, particularly in the energy sector. Sulfur is used in petroleum refining to remove impurities and produce cleaner fuels. Beyond traditional energy, sulfur-based materials are being explored for advanced battery technologies, including lithium-sulfur batteries.
These emerging applications highlight sulfur’s potential beyond conventional manufacturing. While some technologies are still in development, they signal long-term growth opportunities for sulfur producers and chemical manufacturers investing in innovation.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Use
Modern chemical manufacturing places strong emphasis on sustainability, and sulfur plays a role here as well. Many sulfur recovery processes convert byproducts from oil and gas refining into usable industrial sulfur, reducing waste and emissions.
Proper handling and application of sulfur products also help manufacturers meet environmental regulations. Using the right formulation and dosage minimizes byproduct formation and improves overall process efficiency. As regulations tighten globally, suppliers that offer technical support and compliant products provide added value to manufacturers.
Choosing the Right Sulfur Products for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate sulfur product depends on application, purity requirements, handling conditions, and regulatory standards. Manufacturers should work with suppliers who understand their industry and can offer tailored solutions, whether that involves bulk sulfur, sulfuric acid, or specialty sulfur compounds.
Consistent quality, reliable logistics, and technical expertise are just as important as price. In many cases, optimizing sulfur applications leads to better product performance, reduced downtime, and long-term cost savings.
Conclusion
Sulfur applications remain central to modern chemical manufacturing, supporting industries from agriculture and materials to pharmaceuticals and energy. Its versatility, availability, and evolving product forms make it a reliable choice for toko belerang – manufacturers worldwide.
As processes become more advanced and sustainability expectations increase, sulfur-based products will continue to adapt. Companies that understand how to apply sulfur effectively and responsibly will be better positioned to compete in a complex global market.